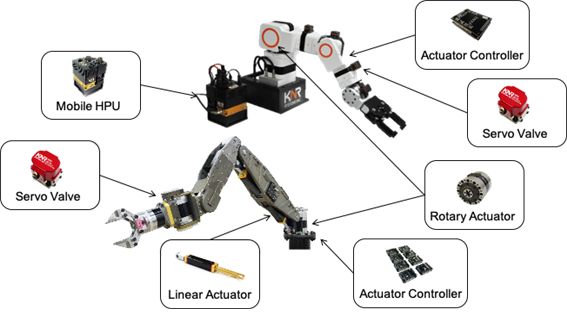
2. Servo valve
The servo valve is a key component in the hydraulic robot configuration that is paired with the actuator to control the flow of hydraulic pressure.
The construction excavator is designed to perform relatively easy tasks, so it consists of a simple valve that can be operated on and off control.
However, hydraulic robots require more precise control, requiring a high-performance servo valve that can control the flow rate quickly and accurately. In addition to performance, the size must be small to attach to the robot, and the price is also important because it requires as many valves as the number of actuators. The size of the servo valve used in robots is about the size of a thumb, but the price is very high and requires high manufacturing technology, so there are only a few suppliers.
Hydraulic servo valve technology needs to be very difficult to implement, especially small servo valves with excellent performance are limited to defense industries such as missiles and rockets, and only five or fewer companies worldwide produce most servo valves. KNR’s servo valve has more than 90% of Moog’s performance, which is a top-notch global company, and has equivalent or higher performance compared to STAR’s servo valve in the UK. It also has price competitiveness compared to its competitors by realizing low manufacturing costs with the latest special manufacturing method.